Much of the atmosphere crossword presents a captivating overview of the Earth’s atmosphere, delving into its composition, structure, and the diverse phenomena that occur within it. This crossword puzzle invites solvers to engage with atmospheric science, testing their knowledge and expanding their understanding of the intricate processes that shape our planet’s aerial envelope.
From the fundamental gases that comprise the atmosphere to the complex interactions that drive weather patterns and climate change, this crossword puzzle offers a comprehensive exploration of atmospheric science. Solvers will encounter clues that challenge their understanding of atmospheric layers, the role of greenhouse gases, and the impacts of human activities on air quality and climate.
The Earth’s Atmosphere
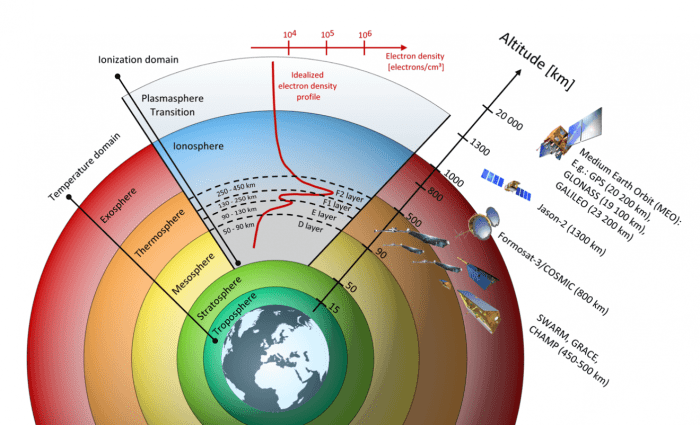
The Earth’s atmosphere is a complex and dynamic layer of gases that surrounds the planet. It plays a crucial role in supporting life and regulating Earth’s climate.
The atmosphere is composed of a mixture of gases, primarily nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and argon (0.9%). Trace amounts of other gases, such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and noble gases, are also present.
Layers of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers, each with its unique characteristics:
- Troposphere:The lowest layer, extending from the Earth’s surface to about 10 km altitude. It contains the majority of atmospheric mass and is where most weather phenomena occur.
- Stratosphere:Lies above the troposphere and extends to about 50 km altitude. It contains the ozone layer, which protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
- Mesosphere:Extends from the stratosphere to about 85 km altitude. It is characterized by decreasing temperature with increasing altitude.
- Thermosphere:The uppermost layer, extending from the mesosphere to about 600 km altitude. It is characterized by extremely high temperatures due to absorption of solar radiation.
- Exosphere:The outermost and thinnest layer, extending beyond the thermosphere. It gradually merges with interplanetary space.
Atmospheric Gases
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere, accounting for approximately 78%. It is essential for plant growth and plays a role in atmospheric pressure and temperature regulation.
Oxygen
Oxygen is the second most abundant gas in the atmosphere, accounting for approximately 21%. It is essential for life and supports respiration in all aerobic organisms.
Argon
Argon is a noble gas that accounts for approximately 0.9% of the atmosphere. It is inert and plays no significant biological role.
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a trace gas in the atmosphere, accounting for about 0.04%. It is essential for plant photosynthesis and plays a role in regulating Earth’s climate.
Water Vapor
Water vapor is a variable component of the atmosphere, ranging from 0-4%. It is responsible for clouds, precipitation, and humidity.
Atmospheric Phenomena

Clouds
Clouds are visible suspensions of water droplets or ice crystals in the atmosphere. They play a crucial role in the water cycle and influence weather patterns.
Precipitation
Precipitation occurs when water vapor in the atmosphere condenses and falls to the Earth’s surface. It can take various forms, including rain, snow, sleet, and hail.
Wind
Wind is the movement of air in the atmosphere. It is caused by differences in air pressure and temperature and plays a role in weather patterns and climate.
Atmospheric Pollution
Sources of Pollution
Atmospheric pollution can originate from natural sources (e.g., volcanic eruptions) and human activities (e.g., burning fossil fuels).
Types of Pollutants
Common atmospheric pollutants include particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and ozone.
Impact of Pollution
Air pollution can have severe impacts on human health, including respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. It can also damage ecosystems and infrastructure.
Climate Change: Much Of The Atmosphere Crossword
Causes of Climate Change
Climate change is primarily driven by human activities that increase the concentration of greenhouse gases (e.g., carbon dioxide, methane) in the atmosphere.
Consequences of Climate Change
Climate change has far-reaching consequences, including rising sea levels, more extreme weather events, and changes in ecosystems.
Role of the Atmosphere, Much of the atmosphere crossword
The atmosphere plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate by absorbing and redistributing heat.
FAQs
What is the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere?
The Earth’s atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and argon (0.93%). Trace amounts of other gases, such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane, are also present.
What are the different layers of the atmosphere?
The atmosphere is divided into five layers: the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Each layer has distinct characteristics, such as temperature, density, and composition.
What causes clouds to form?
Clouds form when water vapor in the air condenses into tiny water droplets or ice crystals. This process occurs when the air becomes saturated with water vapor, often due to changes in temperature or pressure.