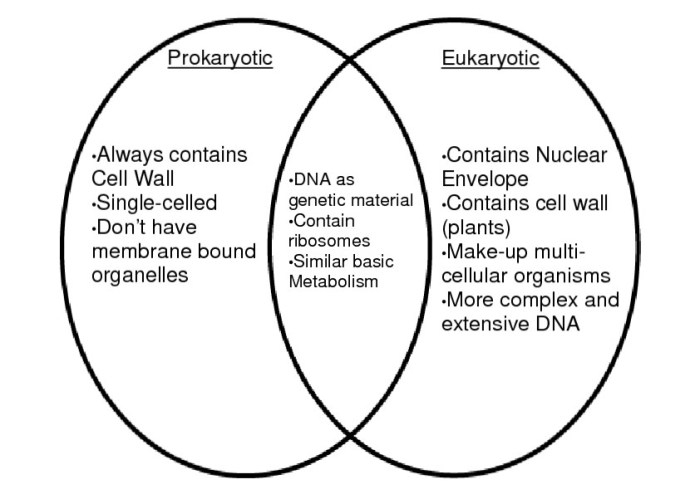
The Venn diagram eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is a visual representation of the similarities and differences between these two types of cells. Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells and have a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and a cytoskeleton. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and do not have these features.
The Venn diagram eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells can be used to compare and contrast the two types of cells in terms of their structure, function, and evolution. This diagram can help students to understand the key differences between these two types of cells and how they are related.
Venn Diagram Overview

A Venn diagram is a graphical representation that displays the logical relationships between different sets of data. It consists of overlapping circles, where each circle represents a set, and the overlapping area represents the intersection of the sets. Venn diagrams are commonly used to compare and contrast different sets of data, identify similarities and differences, and visualize the relationships between them.
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells: Basic Definitions: Venn Diagram Eukaryotic And Prokaryotic Cells
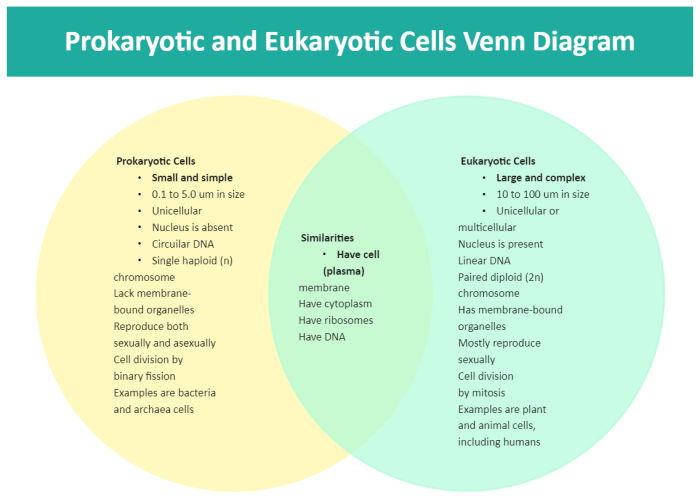
Eukaryotic cellsare complex cells that contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are found in all multicellular organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi. Prokaryotic cellsare simpler cells that lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are found in bacteria and archaea.
Key differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cellsinclude the presence of a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and the size of the cell. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, which contains the cell’s genetic material, while prokaryotic cells do not. Eukaryotic cells also have membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum, while prokaryotic cells do not.
Finally, eukaryotic cells are typically larger than prokaryotic cells.
Structural Differences between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
| Feature | Eukaryotic Cells | Prokaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Present | Absent |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Present | Absent |
| Cell size | Typically larger | Typically smaller |
Functional Differences between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
| Function | Eukaryotic Cells | Prokaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| DNA replication | Occurs in the nucleus | Occurs in the cytoplasm |
| Protein synthesis | Occurs in the cytoplasm | Occurs in the cytoplasm |
| Energy production | Occurs in the mitochondria | Occurs in the cell membrane |
Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells from Prokaryotic Cells, Venn diagram eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
The endosymbiotic theory proposes that eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells through a process of endosymbiosis. Endosymbiosis is the process by which one cell engulfs another cell, and the engulfed cell becomes a symbiotic partner within the host cell. According to the endosymbiotic theory, the mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells were once free-living prokaryotic cells that were engulfed by a larger prokaryotic cell.
Over time, these engulfed cells lost their ability to live independently and became dependent on the host cell for survival.
Examples of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cellsinclude:
- Plant cells
- Animal cells
- Fungal cells
Prokaryotic cellsinclude:
- Bacteria
- Archaea
Detailed FAQs
What is a Venn diagram?
A Venn diagram is a graphical representation of the logical relationships between two or more sets of data.
What are eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
What are prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells are cells that do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
What are the key differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
The key differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells include the presence of a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and a cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells.