Which of the following is the best definition of redistricting? Redistricting is the process of redrawing the boundaries of electoral districts, typically to ensure fair representation and reflect population changes. This process has a significant impact on the political landscape and can affect election outcomes.
Understanding the concept of redistricting is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of electoral systems and ensuring democratic representation.
Redistricting involves dividing a geographical area into smaller electoral districts, each of which elects a representative to a legislative body. The boundaries of these districts are periodically redrawn to account for population shifts and changes in demographics. The goal of redistricting is to create districts that are roughly equal in population and that represent the diversity of the communities they encompass.
Definition of Redistricting
Redistricting refers to the process of redrawing electoral boundaries to adjust the number of voters within each district, ensuring fair representation.
It is the realignment of district lines to reflect population shifts, changes in voter demographics, and legal requirements.
Purpose of Redistricting
Redistricting aims to ensure equal representation for all voters, ensuring that each district has roughly the same number of people.
It helps maintain a balance between rural and urban areas, and protects the voting rights of minority groups.
Methods of Redistricting
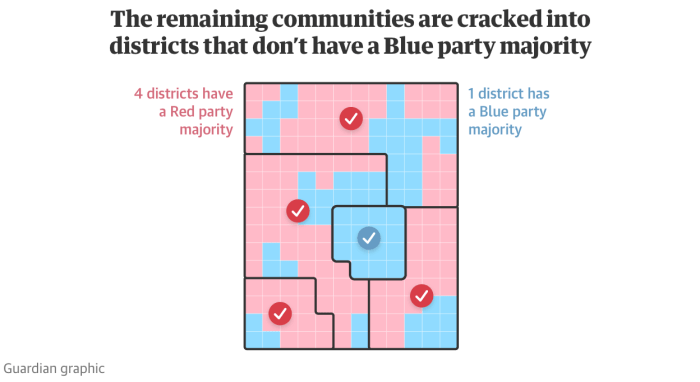
Different methods are used for redistricting, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Geographic Redistricting:Based on geographic boundaries, such as rivers, mountains, or roads.
- Demographic Redistricting:Considers demographic data, such as race, ethnicity, or income, to ensure fair representation of minority groups.
- Political Redistricting:Aims to benefit a particular political party or candidate.
Political Implications of Redistricting
Redistricting can have significant political implications:
- Gerrymandering:The intentional manipulation of district boundaries to favor a particular political party.
- Election Outcomes:Redistricting can influence the outcome of elections by altering the composition of districts.
- Voter Suppression:Redistricting can be used to suppress the voting power of certain groups by diluting their representation.
- Voting Rights Act:Prohibits discriminatory practices in redistricting that dilute the voting power of minority groups.
- Equal Protection Clause:Requires that redistricting be conducted fairly and without bias.
- One Person, One Vote Principle:Ensures that each voter has an equal voice in the electoral process.
- 1812:Gerrymandering was first used in Massachusetts, giving rise to the term.
- 1960s:The Voting Rights Act led to significant changes in redistricting practices to protect minority voting rights.
- 2000s:Advanced technology and data analysis have played a growing role in redistricting.
- Increased Transparency:Efforts to make redistricting processes more open and accountable.
- Data-Driven Redistricting:Use of data analysis to create more accurate and fair district maps.
- Independent Redistricting Commissions:Nonpartisan bodies established to oversee redistricting.
Legal Considerations of Redistricting

Redistricting is subject to legal constraints, including:
Historical Examples of Redistricting: Which Of The Following Is The Best Definition Of Redistricting
Redistricting has a long history in the United States:
Current Trends in Redistricting
Recent trends in redistricting include:
FAQ
What is the primary purpose of redistricting?
The primary purpose of redistricting is to ensure fair representation by dividing a geographical area into electoral districts that are roughly equal in population and that reflect the diversity of the communities they encompass.
How does redistricting affect election outcomes?
Redistricting can significantly affect election outcomes by altering the boundaries of electoral districts and the distribution of voters within those districts. It can create districts that favor certain political parties or candidates, a practice known as gerrymandering.
What are the legal considerations surrounding redistricting?
Redistricting is subject to various legal considerations, including the Voting Rights Act, which prohibits practices that discriminate against minority voters. Courts have also established principles to prevent gerrymandering and ensure that redistricting is conducted in a fair and nonpartisan manner.
