Who is responsible for overseeing a blockchain electronic ledger – In the realm of digital finance and record-keeping, the question of who bears the responsibility for overseeing blockchain electronic ledgers looms large. These decentralized and immutable ledgers underpin a wide range of applications, from cryptocurrencies to supply chain management. Understanding the roles, governance frameworks, and risk management strategies associated with blockchain oversight is crucial for ensuring the integrity and security of these vital systems.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of blockchain oversight, examining the roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders, the governance frameworks that guide their actions, and the risks inherent in managing these complex systems. We also explore industry best practices, successful implementations, and emerging trends that will shape the future of blockchain technology.
Roles and Responsibilities

Overseeing a blockchain electronic ledger requires the collaboration of multiple roles with distinct responsibilities. These roles may include:
- System Architect:Designs and implements the overall blockchain system, including the ledger, consensus mechanism, and security protocols.
- Ledger Administrator:Manages the blockchain ledger, including adding new nodes, maintaining transaction history, and resolving disputes.
- Auditor:Verifies the integrity and accuracy of the blockchain ledger and its transactions.
- Compliance Officer:Ensures that the blockchain system complies with applicable laws and regulations.
- Risk Manager:Identifies and mitigates risks associated with the blockchain system, including cyberattacks, fraud, and data breaches.
Governance and Compliance

The oversight of blockchain electronic ledgers is guided by governance frameworks and compliance requirements. These include:
- Governance Frameworks:Establish principles and guidelines for the management and oversight of blockchain systems. These frameworks may be developed by industry consortia, government agencies, or individual organizations.
- Compliance Requirements:Blockchain systems must comply with applicable laws and regulations, such as data privacy laws, anti-money laundering regulations, and securities laws. These requirements may vary depending on the jurisdiction in which the blockchain system is operated.
Risk Management
Blockchain electronic ledgers are subject to a variety of risks, including:
- Cyberattacks:Blockchain systems can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, such as hacking, malware, and phishing.
- Fraud:Blockchain transactions can be used for fraudulent purposes, such as money laundering, counterfeiting, and identity theft.
- Data Breaches:Blockchain ledgers can contain sensitive data, which could be compromised in a data breach.
Strategies for mitigating these risks include:
- Implementing robust security measures:Blockchain systems should employ strong encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems.
- Establishing clear policies and procedures:Organizations should develop and implement clear policies and procedures for the management and oversight of blockchain systems.
- Conducting regular audits and reviews:Blockchain systems should be regularly audited and reviewed to identify and mitigate risks.
Technology and Infrastructure: Who Is Responsible For Overseeing A Blockchain Electronic Ledger
The oversight of blockchain electronic ledgers is supported by a range of technologies and infrastructure, including:
- Blockchain Protocols:Blockchain protocols define the rules and procedures for creating and maintaining a blockchain ledger. These protocols include consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake.
- Blockchain Platforms:Blockchain platforms provide a software framework for building and deploying blockchain applications. These platforms include Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and R3 Corda.
- Cloud Computing:Blockchain systems can be deployed on cloud computing platforms, which provide scalability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
The challenges and opportunities presented by these technologies include:
- Scalability:Blockchain systems can face scalability challenges as the number of transactions and participants increases.
- Interoperability:Blockchain systems from different providers may not be interoperable, which can hinder the exchange of data and assets.
- Innovation:The rapid pace of innovation in blockchain technology can create challenges for organizations to keep up with the latest developments.
Industry Best Practices
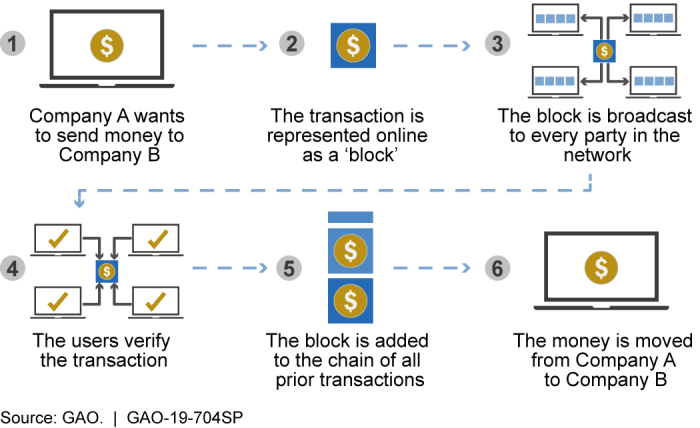
Industry best practices for overseeing blockchain electronic ledgers include:
- Establish clear governance frameworks:Organizations should develop and implement clear governance frameworks for the management and oversight of blockchain systems.
- Conduct regular audits and reviews:Blockchain systems should be regularly audited and reviewed to identify and mitigate risks.
- Implement robust security measures:Blockchain systems should employ strong encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems.
- Collaborate with industry experts:Organizations should collaborate with industry experts to stay up-to-date on the latest developments in blockchain technology and best practices.
Examples of successful implementations of blockchain electronic ledgers include:
- Supply chain management:Blockchain systems are being used to track and trace goods throughout the supply chain, improving transparency and efficiency.
- Financial services:Blockchain systems are being used to streamline financial transactions, reduce costs, and improve security.
- Healthcare:Blockchain systems are being used to securely store and share patient medical records, improving patient care and research.
Future Trends

Emerging trends in the oversight of blockchain electronic ledgers include:
- Increased regulation:Governments are increasingly regulating blockchain systems to protect consumers and ensure financial stability.
- Convergence with other technologies:Blockchain technology is converging with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, creating new opportunities and challenges.
- Decentralized governance:Blockchain systems are becoming more decentralized, with governance and decision-making distributed across multiple participants.
The potential impact of these trends on the future of blockchain technology includes:
- Increased adoption:Increased regulation and the convergence with other technologies are expected to drive the adoption of blockchain technology across a wider range of industries.
- New challenges:The convergence of blockchain technology with other technologies and the increasing complexity of blockchain systems will create new challenges for oversight and governance.
- Transformation of industries:Blockchain technology has the potential to transform industries by creating new business models, improving efficiency, and reducing costs.
Essential Questionnaire
Who is primarily responsible for overseeing a blockchain electronic ledger?
The specific roles and responsibilities for overseeing blockchain electronic ledgers vary depending on the context and industry. However, key stakeholders typically include system administrators, network operators, and governance bodies.
What are the key governance frameworks that guide blockchain oversight?
Governance frameworks for blockchain oversight typically include industry standards, regulatory guidelines, and internal policies established by organizations using blockchain technology.
What are the common risks associated with blockchain electronic ledgers?
Risks associated with blockchain electronic ledgers include security vulnerabilities, operational errors, and compliance challenges.