Peripheral devices normally occupy space inside of the system unit. – Peripheral devices normally occupy space inside of the system unit, serving as essential components that extend the capabilities of a computer system. From input devices like keyboards and mice to storage devices like hard drives, these peripherals play a crucial role in user interaction and data management.
This article delves into the realm of internal peripheral devices, exploring the challenges and techniques involved in optimizing space utilization within the confines of a system unit. We will examine the factors influencing device placement, the consequences of inadequate space, and innovative solutions for maximizing internal space.
Definition of Peripheral Devices
Peripheral devices are components that connect to a computer system and expand its functionality. They typically reside outside the system unit but communicate with the central processing unit (CPU) through various interfaces.
Common peripheral devices include:
- Keyboards: Input devices used for typing text and commands.
- Mice: Input devices used for navigating graphical user interfaces (GUIs).
- Printers: Output devices used for creating hard copies of documents.
- External storage drives: Storage devices used for storing and retrieving data, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs).
Internal vs. External Peripheral Devices
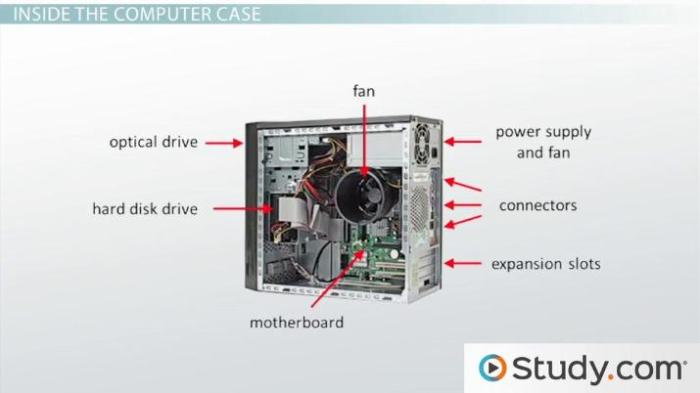
Peripheral devices can be classified into two types based on their physical location relative to the system unit:
Internal Peripheral Devices
Internal peripheral devices are installed inside the system unit. They are typically connected to the motherboard via expansion slots or headers.
Advantages:
- Faster data transfer rates due to direct connection to the motherboard.
- Protected from external elements, ensuring reliability.
Disadvantages:
- Limited space within the system unit.
- Difficult to install and remove.
External Peripheral Devices, Peripheral devices normally occupy space inside of the system unit.
External peripheral devices are connected to the computer system via external ports, such as USB, FireWire, or Thunderbolt.
Advantages:
- Easy to install and remove.
- Can be used with multiple computers.
Disadvantages:
- Slower data transfer rates compared to internal devices.
- More susceptible to damage from external elements.
Space Considerations for Internal Peripheral Devices
The physical constraints of the system unit limit the number and size of internal peripheral devices that can be installed.
Factors to consider:
- Device size:Larger devices require more space.
- Device shape:Odd-shaped devices may be difficult to fit.
- Power requirements:High-power devices may need additional cooling.
Typical organization:
- Motherboard: Houses essential components like the CPU and memory.
- Expansion slots: Allow for the installation of additional cards, such as graphics cards and sound cards.
- Storage bays: Accommodate storage devices like HDDs and SSDs.
Space-Saving Techniques for Internal Peripheral Devices
Several methods can be employed to minimize the space occupied by internal peripheral devices:
- Compact devices:Designed with smaller footprints to fit into tight spaces.
- Modular devices:Can be disassembled into smaller components for easier installation.
- Vertical mounting:Devices can be mounted vertically to save horizontal space.
- Stackable devices:Some devices can be stacked on top of each other.
Examples of Peripheral Devices that Occupy Internal Space: Peripheral Devices Normally Occupy Space Inside Of The System Unit.
| Device Name | Type | Function | Typical Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphics card | Display adapter | Renders and outputs graphics | Expansion slot |
| Sound card | Audio adapter | Processes and outputs audio | Expansion slot |
| Hard disk drive (HDD) | Storage device | Stores and retrieves data | Storage bay |
| Solid-state drive (SSD) | Storage device | Stores and retrieves data faster than HDDs | Storage bay |
Consequences of Inadequate Space for Internal Peripheral Devices
Insufficient space for internal peripheral devices can lead to several issues:
- Overheating:Crowded devices can block airflow, leading to overheating.
- Airflow restrictions:Blocked airflow can impair cooling, affecting system performance.
- Device conflicts:Overlapping devices can cause physical conflicts or resource conflicts.
- Reduced performance:Overheating and airflow restrictions can degrade system performance.
- Increased risk of failure:Overheated or damaged devices are more likely to fail.
FAQ Explained
What are the advantages of using internal peripheral devices?
Internal peripheral devices offer several advantages, including increased speed and reliability due to direct connection to the motherboard, better protection from external elements, and a more organized and aesthetically pleasing system build.
What are the consequences of inadequate space for internal peripheral devices?
Insufficient space for internal peripheral devices can lead to overheating, airflow restrictions, device conflicts, and reduced system performance and reliability.
What are some space-saving techniques for internal peripheral devices?
Space-saving techniques include using compact or modular devices, vertical mounting, stackable devices, and cable management solutions.