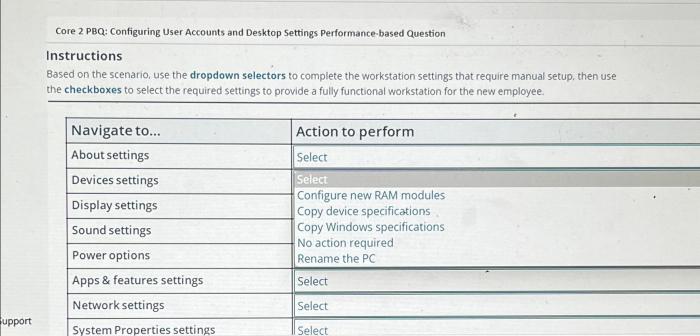
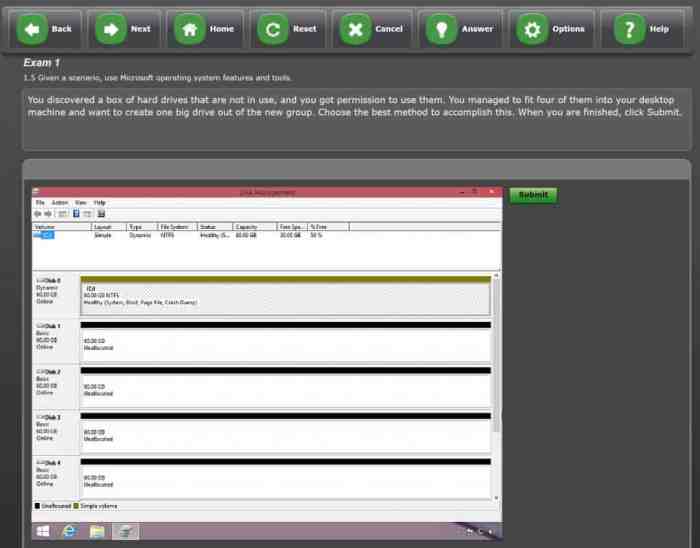
Core 2 pbq: troubleshooting windows os problems performance-based question – In the realm of computer troubleshooting, the Core 2 PBQ stands as a comprehensive assessment of one’s ability to diagnose and resolve performance-related issues within Windows operating systems. This guide delves into the intricacies of performance optimization, hardware-related concerns, software-related challenges, and advanced troubleshooting techniques, empowering readers to tackle even the most complex performance bottlenecks.
Troubleshooting Windows OS Performance Problems: Core 2 Pbq: Troubleshooting Windows Os Problems Performance-based Question
Windows operating systems are widely used, but they can encounter various performance issues. These problems can manifest in slow boot times, application freezes, and general sluggishness, impacting user productivity and satisfaction.
Common Performance Issues in Windows OS
- Slow boot times: Windows OS can take a long time to boot due to various factors, such as a large number of startup programs or outdated drivers.
- Application freezes: Applications may freeze or become unresponsive, hindering user tasks and causing frustration.
- General sluggishness: The entire system may feel slow and unresponsive, affecting overall user experience.
Troubleshooting Performance-Based Questions
When troubleshooting performance-based questions, it is crucial to understand the problem’s context. Gather system information, such as hardware specifications and software configurations, to identify potential bottlenecks.
Diagnostic tools and performance monitors can be used to analyze system behavior and pinpoint performance issues. By monitoring metrics like CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk activity, you can identify areas for improvement.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Optimizing system performance involves various techniques. Disabling unnecessary services and programs reduces resource consumption and improves overall responsiveness.
Adjusting power settings can balance performance and battery life. Managing virtual memory ensures sufficient memory for applications to run smoothly.
Regular system maintenance, including disk cleanup and registry optimization, helps remove unnecessary files and optimize system configurations, contributing to improved performance.
Hardware-Related Performance Issues
Outdated or insufficient hardware can significantly impact performance. Identify hardware bottlenecks, such as slow hard drives or limited RAM, by monitoring system metrics and analyzing performance data.
Upgrading or replacing hardware components can address performance limitations. Consider factors like CPU speed, RAM capacity, and storage type when making hardware upgrades.
Software-Related Performance Issues, Core 2 pbq: troubleshooting windows os problems performance-based question
Poorly optimized software can affect performance. Malware infections, outdated drivers, and software conflicts can cause system slowdowns and instability.
Identifying and resolving software-related performance problems involves updating drivers, removing malware, and troubleshooting software compatibility issues.
Advanced Performance Troubleshooting
Complex performance issues may require advanced troubleshooting techniques. Performance profiling tools provide detailed information about application behavior, helping identify performance bottlenecks.
Analyzing system logs can reveal errors and performance-related events. Memory leak detection and resolution techniques are essential for addressing memory-related performance issues.
Answers to Common Questions
What are common performance issues encountered in Windows OS?
Common performance issues include slow boot times, application freezes, general sluggishness, and system instability.
How can I gather system information for troubleshooting performance issues?
To gather system information, use tools such as System Information (msinfo32) and Task Manager. Check hardware specifications, software configurations, and resource utilization.
What are some methods for optimizing system performance?
Disable unnecessary services and programs, adjust power settings, manage virtual memory, and perform regular system maintenance tasks like disk cleanup and registry optimization.