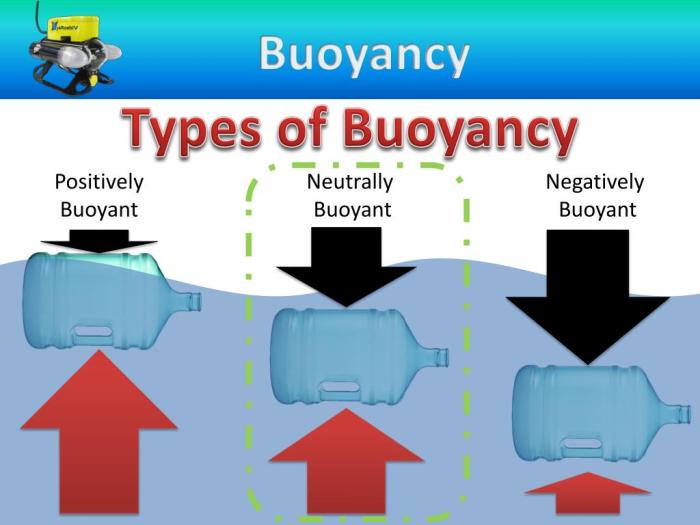
If an object is neutrally buoyant in fresh water, it exerts an upward buoyant force equal to its weight, causing it to float without sinking or rising. Understanding the concept of neutral buoyancy is crucial for various applications, including underwater exploration and marine research.
This article delves into the factors affecting an object’s buoyancy, methods for measuring it, and its significance in marine life and other fluids.
Object Buoyancy in Fresh Water
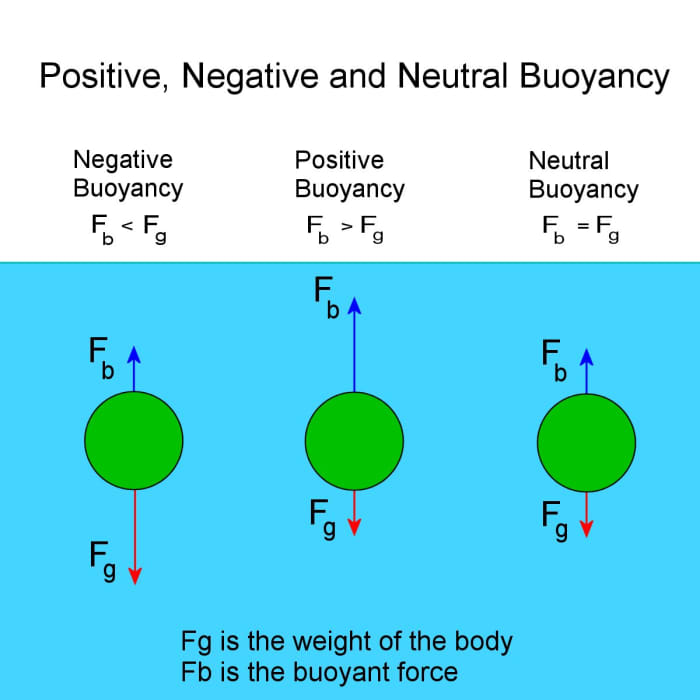
Buoyancy refers to the upward force exerted on an object submerged in a fluid, such as water. This force opposes the object’s weight and determines whether it floats, sinks, or remains suspended.
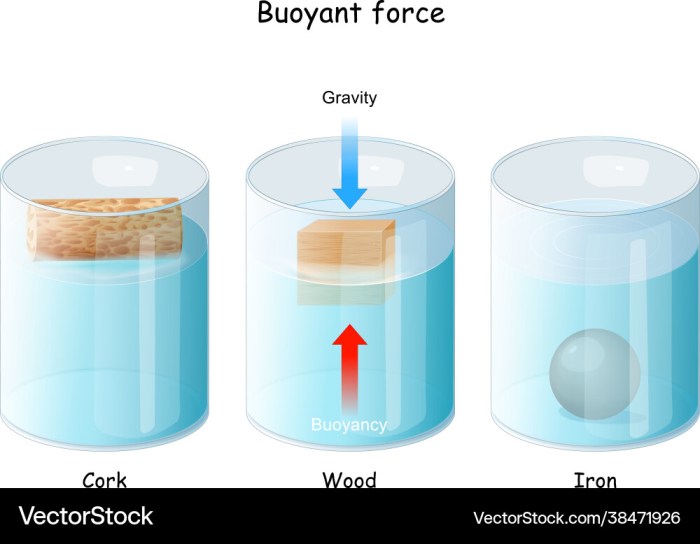
The buoyancy of an object in water depends on two factors: its density and shape. Density is the mass per unit volume, and objects with a density less than that of water will float, while objects with a density greater than that of water will sink.
Shape also plays a role in buoyancy, as objects with a larger surface area experience greater upward force. This is because the surface area of an object determines the amount of water it displaces, which in turn affects the buoyancy force.
Examples of Objects Neutrally Buoyant in Fresh Water, If an object is neutrally buoyant in fresh water
- Wood:Wood has a density slightly less than that of water, which allows it to float on the surface.
- Cork:Cork has a very low density, making it one of the most buoyant materials known.
- Certain types of plastic:Some plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, have densities close to that of water, allowing them to float.
Measuring Neutral Buoyancy
To measure the buoyancy of an object in fresh water, several methods can be employed:
- Hydrostatic weighing:This method involves weighing an object in air and then in water. The difference in weight is equal to the buoyancy force.
- Volume displacement:This method involves submerging an object in a graduated cylinder filled with water and measuring the increase in water volume. The volume of the displaced water is equal to the volume of the object.
- Hydrometer:A hydrometer is a device that measures the specific gravity of a liquid. It can be used to determine the density of an object by measuring the depth to which it sinks in water.
Once the buoyancy force is known, the density of the object can be calculated using the following formula:
Density = Buoyancy force / Volume of displaced water
Accurate measurements are crucial for determining neutral buoyancy, as even small deviations can affect the object’s ability to float.
Applications of Neutral Buoyancy: If An Object Is Neutrally Buoyant In Fresh Water
Neutral buoyancy has numerous applications, particularly in underwater exploration and marine research:
- Submarines:Submarines achieve neutral buoyancy by adjusting their ballast tanks to match the density of the surrounding water, allowing them to remain submerged at a specific depth.
- Buoyancy compensators:Divers use buoyancy compensators to control their buoyancy while underwater. By adding or releasing air, they can adjust their density to match that of the water.
- Marine research:Scientists use neutrally buoyant floats to collect data from the ocean. These floats drift with the currents, providing information about temperature, salinity, and other parameters.
Neutral buoyancy allows objects to float freely without sinking or rising, making it essential for these applications.
Implications for Marine Life
Neutral buoyancy is crucial for the survival of many marine organisms:
- Fish:Fish have evolved swim bladders, which they use to control their buoyancy and maintain a specific depth.
- Plankton:Plankton are small organisms that float in the water column. They have adaptations that reduce their density, such as large surface areas or oil droplets.
- Jellyfish:Jellyfish have a low density due to their high water content, which allows them to float effortlessly.
Changes in buoyancy can have significant consequences for marine ecosystems, as organisms may not be able to maintain their optimal depth or distribution.
Neutral Buoyancy in Other Fluids
Neutral buoyancy is not limited to fresh water. It also applies to other fluids, such as saltwater or air:
- Saltwater:The density of saltwater is higher than that of fresh water, so objects will have greater buoyancy in saltwater.
- Air:The density of air is much lower than that of water, so objects will have much greater buoyancy in air.
Neutral buoyancy is essential in applications such as hot air balloons, which float in the air due to their low density compared to the surrounding air.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of neutral buoyancy in marine life?
Neutral buoyancy is essential for many marine organisms, allowing them to float effortlessly at a desired depth without expending energy on swimming or maintaining their position.
How is neutral buoyancy measured?
The buoyancy of an object can be measured using various methods, such as the Archimedes principle, which involves immersing the object in a fluid and measuring the displaced fluid’s weight.
What are the advantages of using neutrally buoyant objects in underwater applications?
Neutrally buoyant objects can move freely underwater without sinking or rising, making them ideal for tasks such as underwater exploration, photography, and scientific research.